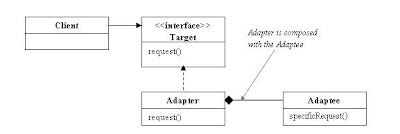
- The adapter acts as the middleman by receiving requests from the client and converting them into requests that make sense on the vendor classes
- The adapter implements the target interface and holds an instance of the adaptee
- The actual interface that the client needs is the target interface
- We wrap the target interface with an adaptee interface, which does the work of the target interface
- The client makes the request on the adapter, and the adapter delegates it to the adaptee interface
- The client doesn't know that the actual work was done by the adaptee
- Client and the adaptee are decoupled – neither knows about the other
- Here's how the client uses the adapter
o The client makes a request to the adapter by calling a method on it using the target interface
o The adapter translates that request into one or more calls on the adaptee using the adaptee interface
o The client receives the results of the call and never knows there is an adapter doing the translation
- The Adapter Pattern converts the interface of a class into another interface the clients expect
- Adapter lets classes work together that couldn't otherwise because of incompatible interfaces
- This decouples the client from the implemented interface,
- If the interface changes over time, the adapter encapsulates the change so that the client doesn't have to be modified each time it needs to operate against a different interface
- It is not necessary that the adapter should wrap only one adaptee – it can hold two or more adaptees that are need to implement the target interface
- There are two types of adapters
o object adapters – uses composition - the adapter is composed of adaptee
§ it can not only adapt an adaptee class, but any of its subclasses
o class adapters – uses multiple inheritance - the adapter subclasses both the target and the adaptee
§ it is committed to one specific adaptee class, but it doesn't have to reimplement the entire adaptee
§ it can also override the behavior of the adaptee, since its just subclassing
§ this cannot be used in Java since it involves multiple inheritance
- Although Decorator and Adapter patterns looks similar, they are totally different in intent
o Decorator wraps an object and adds new behavior
o Adapter wraps an object and converts it into an interface the client expects
- Following is an example of Adapter pattern. This example adapts an Enumerator to act as an Iterator
public class EnumerationAdapter implements Iterator {
Enumeration enumeration;
public EnumerationAdapter(Enumeration enumeration) {
this.enumeration = enumeration;
}
public boolean hasNext() {
enumeration.hasMoreElements();
}
public Object next() {
enumeration.nextElement();
}
public void remove() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
}

No comments:
Post a Comment